How Does a Barcode Work?
How Does a Barcode Work?
How Does a Barcode Work?
8 Jan 2024
 Aptean Staff Writer
Aptean Staff Writer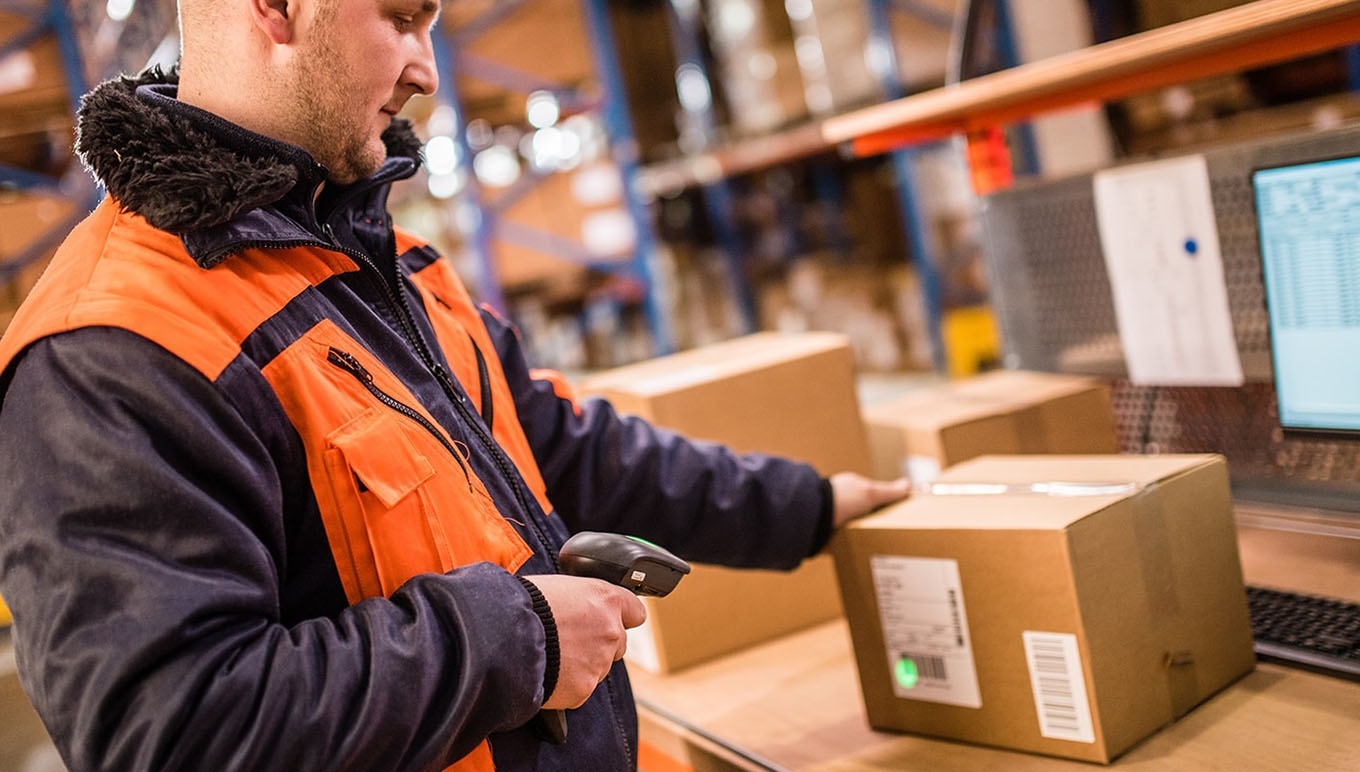 
If you are completely new to how barcodes work, we are here to help. You may have an existing barcode system and want to know how to expand it or optimise it better, or perhaps you want to upgrade to a more sophisticated barcode system.
For expert advice and assistance on how to upgrade your barcode system, or to install a barcode system for the first time to make your business commercially successful, contact Aptean for the best professional advice. We invite you to compare all the various barcode reader systems and WMS software options.
What Is a Barcode in Simple Terms?
Barcodes use modern technology to store vast amounts of information about products, manufacturers, distributors and shipping details, in coded form on a label the size of a postage stamp or smaller.
Barcode scanners read these codes from labels adhered to each product and send them to a computer equipped with sophisticated software that analyses, interprets, computes, and updates the data, all in a fraction of a second, and prints any paperwork you require.
In a modern world, where improved transaction speed, accuracy of storage and real-time data updating are imperative to the success of any business, we can no longer operate with manually updated systems and processes. Manual systems are prone to errors, are cumbersome and time-consuming, and are not cost-effective.
Barcodes have become ubiquitous in any business and we see them on groceries, library books, airline tickets, software applications, delivery notes, invoices, spare parts, and in fact, on virtually everything we use in our daily lives.
No warehouse, retail store, wholesale store, convenience store, manufacturer, distributor, or online business can afford to be without a barcoding system.
What Do All the Lines, Dashes, Dots, Spaces, Shapes, Numerals, and Characters on a Barcode Label Mean?
Think of a highly sophisticated Morse Code that uses all kinds of machine-readable representations to code and decode vast amounts of information. This information includes details about item descriptions, size and dimensions, colour, price, markup and profit margin, discount tiers, stock levels, manufacturer’s and supply chain details, location on your warehouse shelves, all manner of instructions, software applications, and much more.
Each of the lines of various thicknesses and lengths, dashes, dots, spaces of different widths, and a variety of geometric shapes, numerals, and characters, is assigned a special meaning by a computer, much like letters of the alphabet in different positions would spell different words, and these patterns are then printed onto labels.
The outer two lines and the one in the centre, are called guard bars which tell the computer and barcode scanner when the codes begin and end, and the two numbers outside the white bars of the guard tell the software whether the code is the right way up.
A barcode scanner reads the pattern on the barcode label and sends it to a computer that decodes the pattern and gives you all the information you require about the product, and the information can be printed on a screen or paper in ordinary language.
How Does a Barcode Scanner Read a Barcode Label?
An Incandescent Light Bulb or Laser Light
Most barcode scanners use a laser light or incandescent light bulb to illuminate the barcode label. The black parts of the pattern absorb the light while the light is either reflected or shines through the white parts, onto a super-sensitive light detector that detects and analyses the light pattern.
When using laser scanners, laser beams are reflected off a mirror, sweeping across the label to read the barcode. This allows reading wider barcodes and from further away.
The scanning engine translates the light impulse into data, much the same as your computer screen or smart device translates an electric impulse typed on the keyboard, into digits you can read.
Range of Barcode Scanners
Barcode scanners vary in complexity and sophistication. Most smart devices can read barcodes, up the scale to two-dimensional area barcode scanners which take detailed pictures of any barcode and analyse them.
These scan engines can capture the picture in any direction and are highly accurate and super fast.
What Are the Different Types of Barcode Systems?
Different types of barcodes are used, depending on the complexity of the product and the amount of information that needs to be stored on the barcode label.
This information is used for identifying products, inventory tracking, locating specific items, ordering new stock, inventory control, point-of-sale, pricing, profit margins, discount levels, tracking inventory amounts, and much more.
Numeric and alpha-numeric barcodes.
The first tier consists of one-dimensional labels using numeric or alpha-numeric digits, characters, lines, and spaces of varying widths, and 95 evenly spaced columns, on a white background, each representing separate, detailed data.
UPC and EAN Barcodes
The most common barcodes, named UPC (Universal Product Code) and EAN (Originally European Article Number, but this has been extended to International Article Number codes, set by the global standards organization and used in global trade) use a 12- or 13-digit number that represents different types of data.
The first number is the product type, the following 5 numbers are a unique identifier of the manufacturer code or distributor code, the next 5 numbers describe the particular product, and the final number is a self-checking digit that allows the barcode reader and computer to determine if the barcode is correctly composed.
Code 39 and 128 Barcodes
Code 39 and 128 barcodes contain variable numbers of digits or characters, depending on the amount of data required but like the UPC barcodes and EAN barcodes, each barcode and set of numbers or digits denote specific types of information.
Code 39 uses 43 characters, consisting of uppercase letters, numeric digits, and special characters. Code 128 is a high-density, barcode technology that uses alphanumeric or numeric-only characters which can encode all 128 ASCII characters.
Two-Dimensional QR and Data Matrix Codes
QR codes (quick response codes) are used for more complex data storage and in addition, have interactive capabilities, redirecting the user to a website, online user manual, or app store.
QR codes and data matrix codes make use of a complex combination of short lines, dots, and geometric shapes arranged in a grid, while some include data matrix codes which are used in electronics and logistics.
They are called two-dimensional because hundreds of times more information can be stored on both the vertical and horizontal planes. 2D codes are omnidirectional and can be read from any angle.
Uses of Qr and Data Matrix Codes
QR and data matrix codes are very popular in wholesale, retail, and computer application industries because they can be scanned by consumers with smartphones.
They can store information such as brand name, model number, maintenance records, telephone numbers, login details, online account information, and links to websites.
They are also widely used for warehouse inventory management software, maintenance, transportation, health and medical industries, the travel industry, software applications and playstores.
PDF417 Code
PDF-417 is a specialist rectangular 2D barcode that uses stacked linear rows of up to 90, each of which is comparable to a linear barcode.
PDF is a common data format and the “417” indicates that the visual pattern consists of 4 bars of black and white bars in space in a pattern that is 17 modules long.
What Are PD417 Codes Used For?
Because they store personal and other important additional data and are extremely useful in document management, they are commonly used in driver’s licences, ID cards, passports, the transportation industry, and in certain warehouses for inventory management.
How Are Barcodes Generated?
There is special software that automatically generates unique machine-readable barcodes for each individual product, using information entered by the user.
Why Should Your Warehouse Use Barcodes?
No business is too small to benefit from barcodes to improve efficiency and enhance the professional image of your business.
Cost-Effective and Easy-To-Install
A barcoding system is relatively cheap to install and maintain, and will more than pay for itself in providing quick and accurate information at the point of sale, inventory management, and supply chain management.
A barcoding system can be fully integrated with Aptean WMS software as a cost-effective modular add-on.
Benefits of Barcodes
For inventory management, an integrated barcode system eliminates the need to manually count and record individual products and drastically reduces the chances of human error.
You can digitally store vast amounts of sales data and other important information about each product in your warehouse, which is instantly available to streamline operations and maximise profits.
Unlike paper records which are incredibly cumbersome to maintain, digital barcode data takes up absolutely no physical space.
Staff Training
It is important to train staff how to effectively and efficiently use the barcode system, but it is incredibly easy to understand and training will not take long.
Most modern barcode scanners are incredibly user-friendly and can easily be managed by even the least tech-savvy employee.
What Are the Disadvantages of Barcodes?
Human Error
If an error is made in creating the barcode, it might well affect the entire product range, but once identified, is quick and easy to correct on the system.
It is good practice to double-check all entries before generating the barcode labels. Sophisticated barcoding software, has error-checking capabilities, further reducing human error.
Cost of Hardware
Depending on the nature of your business, several expensive barcode scanners and other hardware may be required. Once again, the benefits by far outweigh the disadvantages of the capital costs and in terms of efficiency and labour saving, they will soon pay for themselves too.
Damaged or Faded Labels
If barcode labels fade or are damaged, it will be difficult to identify the product. It is very important to ensure the correct labels are adhered to the product in a position that is easily located and read by the barcode scanner.
Frequently inspect the labels and ensure they synchronise with the software system. When special offers or seasonal changes, temporarily change the price or other information about the product code, ensure the system is amended accordingly.
How Will a Barcode System Help My Business?
There are so many ways in which a barcode system will benefit your business, but here are a few of the most important functions:
Inventory Identification and Tracking
Barcodes make it a simple matter to enter new items into your own inventory tracking database and keep track of the location, all movements, stock levels, orders, shipping, and delivery.
Invoicing
Barcodes can be linked to orders and invoices for greater accuracy, expediting the fulfilment process, and automatically adjusting stock levels.
The operator simply needs to scan the barcode on the invoice to locate items for picking, where they are located, and what equipment is required to access and package the items for delivery.
Shipping and Delivery
By scanning the barcode upon acceptance for shipping or delivery, the operator will instantly identify the correct parcel. It makes it simple to accurately keep track of the delivery status.
Storage, Picking and Shipping Merges
Barcodes can easily be created for batches of products, linking them to each other according to the data fields you choose.
Is There an Alternative to Barcodes?
RFID (Radio frequency identification) is a fully automated alternative to barcodes.
Which Is the Best Barcode System for My Business?
Your choice will enable you to make better business decisions, streamline your operations, and speed up your service delivery.
How to Set Up a Barcode System for the Warehouse
This comprehensive guide is designed to show you how to set up a barcode system for the warehouse. For over three decades, Aptean has been dedicated to the continuous development and enhancement of Empirica WMS, transforming it into a renowned Warehouse Management System.
What Is a Barcode System?
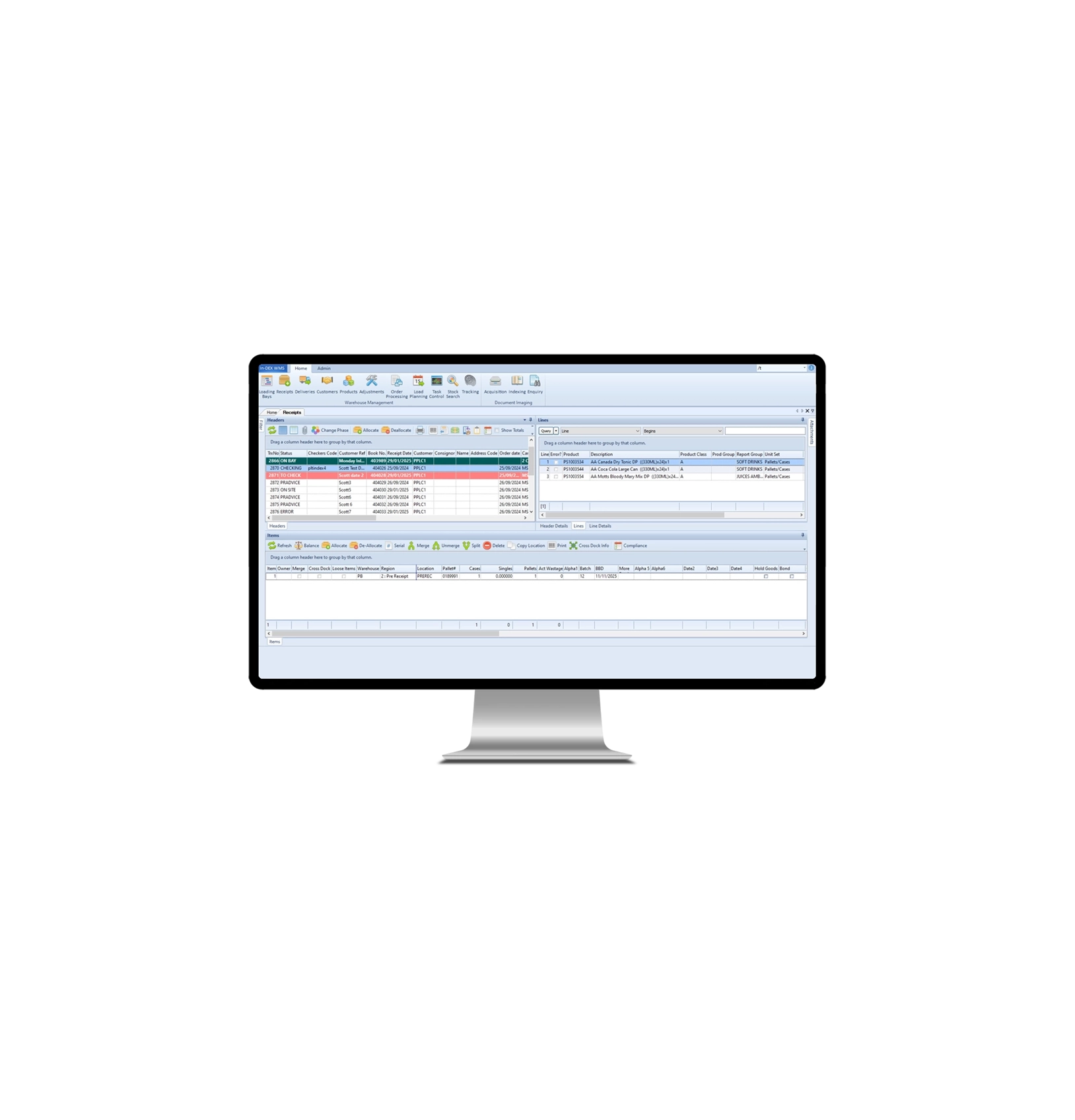
Barcode systems are ubiquitous in any warehouse and store in the 21st century. Huge amounts of automated data about individual products are captured in code, made up of numbers and lines, created by computer software, printed on labels and adhered to the stock items.
Sophisticated scanners can read this code and send it back to a computer where the specialised software interprets the code and updates the information to control and track inventory.
A barcode system makes it possible to automate data collection and control at levels not possible otherwise. Rather than manually writing or typing information on labels, the barcodes encrypt vast amounts of information on a small label for fast transfer to a computer by means of a scanner, which can be mobile and handheld. Once interpreted by the computer, this information can be printed on invoices, inventories, shipping documents, and much more.
How Was the Barcode System Invented?
Virtually since the Industrial Revolution and the development of trade, it has been a challenge to effectively control inventory and keep accurate track of stock levels and sales. This conundrum led to the first barcode in 1948, designed like a bullseye with reflective lines, that only worked in the laboratory because of the technological limitations of the time and the first practical implementation of a linear barcode was introduced in the 1960s to track rail cars in the USA. Only in 1974 did the invention of lasers and integrated circuits make it possible for RCA and IBM to develop barcodes suitable for retail, but it was not until the 1980s that the Universal Product Code (UPC barcode) was widely adopted in supermarkets. This greatly sped up checkout and improved the accuracy of the checkout, reduced fraud and theft, accurately monitored sales in real-time, and the ability to generate reports for stock audits and inventory management. The dot-com boom merged the digital and physical world and together with smart technology, the retail world evolved into a new universe of online shopping and warehousing, making barcoding indispensable to track assets and asset movement throughout the supply chain.
Why Do You Need a Barcoding System?
It is no longer possible to keep up with the fast pace of business and meet customer demands without using the best technology available. Warehousing management systems (WMS) have made warehouses much more efficient, productive, and profitable. A barcoding system is a vital component of an effective WMS, saving costs and labour; minimising lost inventory; accurately recording and transferring information; simplifying goods receiving, stock identification, picking, and shipping; and maximising storage space.
Can You Manage a Warehouse Without a Barcoding System?
Warehouse management systems can function quite well without barcoding, but the question is whether your business can afford to be without it. Tiny suburban shops or kiosks, and warehouses with an uncomplicated inventory, might still survive without barcodes in the 21st century but it is unthinkable that you can manage a warehouse, distribution centre, 3PL logistics, or eCommerce business of any substance and complex inventory without it. Your supply chain partners, vendors, and third-party customers will often demand the use of barcodes that can be integrated with theirs in the supply chain.
What Is the Difference Between a Barcoding System and an RFID System?
These two systems in essence do the same work, which is to track and manage inventory, but use different technologies, and it is not uncommon to see both systems in use in a warehouse. Barcode readers use laser light technology to read the barcode patterns on labels, while RFID (radio frequency identification) uses radio waves to retrieve and transmit data from electronic tags or microchips.
What Do You Need to Know Before You Purchase and Set Up a Barcode System?
Decide whether you need a barcoding system, an RFID system or a combination of both systems. Familiarise yourself with the different types of barcoding and labelling systems, and get to understand automatic data collection devices and software. Decide how best to integrate your barcoding system with your WMS software and your business procedures. Select the best type of barcoding system for your warehouse from these main types:
Numeric Barcoding Systems
This is known as a one-dimensional system because it comprises only numbers and bars of various widths and spacings, capturing information like product identity, and manufacturer’s information. Three of the numeric barcode systems, namely, Universal Product Number (UPC); Interleaved, and International Article Number, are widely used in retail, warehousing, telecommunications, and airlines for inventory flow and point of sale. A widely used version of numeric barcoding systems is Code 39.
Alphanumeric Barcoding Systems
This barcoding system consists of a combination of numbers and letters and bars of various widths and spacings. Code 128 is one of the alphanumeric barcoding systems most widely used in warehousing and supply chain operations because of its compact high-density codes which can store vast amounts of diverse information.
Two-Dimensional Qr Code or Data Matrix Barcoding Systems
QR (which means “quick response”) codes usually have a square or rectangular shape with a combination of short lines, dots, and geometric shapes, while some include data matrix codes used in electronics and logistics. They are called two-dimensional because hundreds of times more information can be stored on both the vertical and horizontal planes. They are very popular in the shopping and computer application industries because they can be scanned by consumers with smartphones. They can store information such as brand name, model number, maintenance records, telephone numbers, login details, online account information, and links to websites. QR codes are also widely used for warehouse inventory management, maintenance, transportation, the travel industry, software applications and play stores. Data Matrix barcoding can also contain serial numbers, lot numbers, production dates, expiry dates, etc.
Steps to Set Up Your Barcode System in a Warehouse
Choose the Type of Barcoding System That Will Best Suit Your Warehouse
Decide whether you want to use a numeric, alphanumeric, or QR barcoding system. Factors like the complexity and volumes of your inventory, the cost to implement the system, etc. will need to be considered. Define which information is important to your warehousing operations to maximise workflow and efficiency. As an example, you could include information like stock codes, item descriptions, specifications, product and storage or shipping dimensions, weight, manufacturer’s details, country of origin, supplier details, purchase price, date of purchase, lot numbers, quantities in stock, stock levels required, resale price, discount levels, expiry dates, tracking information, shipping and logistics partners, seasonal popularity, etc.
Choose the Correct Barcoding Software System to Integrate With Your WMS
Aptean perfectly integrates with almost any barcoding system and expands your options to voice picking, RFID, and much more. With budget constraints, it might be advisable to purchase modular software such as Aptean, adding functions as you need them.
Choose the Most Suitable Scanners and Scan Engines That Match Your WMS and Barcoding System
Warehouse scanners are usually mobile devices that read the barcodes on your tags, and send the information to the barcode scan engine for analysis. The scan engine analyses and decodes different barcode labels, using the software on your computer. Decide which type of scanner and scan engine will work best for your warehouse, also bearing in mind durability, ease of use, serviceability and finding replacement or expansion components. Do you require wireless technology? Which type will integrate best with your existing and other warehouse management software? How far do the scanners need to be from the barcode label for accurate scanning? Some need to be held close to the label, while others have a floor-to-ceiling capability. There are three main types of scan engines, laser, linear imager, and area imager. A laser scan engine uses an optical system with a moving mirror to make the laser line which is reflected onto a photodiode and a processor that decodes the light signal and outputs the decoded data via a serial interface, USB, Bluetooth or wireless port. A linear imager scan engine takes a picture of the barcode, which is analysed and decoded by the scan engine, and the decoded data is output via a serial interface, USB, Bluetooth, or wireless port. An array imager scan engine has the capability to handle OCR, document, and image capturing, and can scan two-dimensional barcodes. Output can be via serial interface, USB, Bluetooth, or wireless port.
Generate Codes for All Your Stock Items and Their Variants
All the information about the product, such as physical description, specific model, measurements, purchase cost, manufacturer and vendor information, minimum stock required in your inventory, etc. is entered into the software. The first step for most warehouses starting this process is to set up a product list on a spreadsheet, listing all the information that you can tie to the barcodes for each product. At first, this seems a daunting task but it can be done in baby steps, starting with all new transactions, pick slips, purchase orders, and key products. You can then proceed in stages to incorporate the rest of your inventory per category until the job is completed. Your WMS will record every new addition and update your automated inventory. In the interim, you can run the automated and manual systems in parallel. Once all the information has been entered into the software, these codes are computer-generated by the software, giving each inventory item a unique alphanumeric code identifier, known as a Stock Keeping Unit or SKU, to identify and track that item. It might be wise to synchronise your barcodes with those of your other partners in the supply chain for greater efficiency and seamless transactions. Specialist barcode generators are included in some of the software, while others offer an online service, often for free.
Label Your Inventory
Decide if you want to label your inventory in batches or relabel all stock items in one go during a stocktake. The codes generated by your software system are then printed on labels or tags that are adhered to the product and usually also a location identifier on the shelf. Remember that the location of an item is often more important than the product description to easily access, pick or ship orders. Specialist barcode design and printer functions are included in the top software, while others offer it as an add-on. Bear in mind physical factors that might affect your barcode labels and cause deterioration. Is your inventory exposed to extreme heat or cold, moisture, sunlight, abrasion, etc.?
Integrate Your WMS Warehouse Management Software and Barcode System
Your warehouse management system (WMS) , manages and integrates all the technology in your warehouse operations.
It identifies the data from the scanner and engine, confirms the accuracy and instantly computes all the information in real-time. You can generate reports, invoices, shipping manifests, etc. at the push of a button.
Aptean easily and fully integrates with a warehouse barcoding system and other software platforms. It collates all data to manage receipts, storage, picking, rotation, and dispatching of inventory items, generating detailed reports which are instantly and securely available from a smart device.
Put Your Barcoding Inventory Into Operation
Map out the warehouse layout to optimise storage, travel distances for picking, and maximising workflow. It is usually best to work as a team, taking advice from the people who are on the floor and will be using the system. This will create a better understanding of the process and help to get your staff to buy into the new system. It is now time to pack all your inventory items in the allocated spaces while optimising storage and travel distances for picking.
Train your staff to effectively and efficiently use the barcode system.
Stock can now be audited with the greatest of ease and accurate records are kept of inventory and timeous placement for replenishment orders.
You will immediately enjoy considerable benefits when migrating from a manual or paper-based system, which includes greater efficiency, cost and time savings for labour, accurate inventory, accurate picking and shipping, improved workflow, greater visibility and instant access to information required for strategic management decisions.
Review your processes regularly to ensure you are still doing business most efficiently and cost-effectively.
Find out more about our cost-effective, versatile and fully featured WMS software suite, designed to meet the diverse needs of your business. Contact us today or request a demo.
Want to see our WMS software in action?
Request your short demo with one of our experts and see for yourself how ProWMS could improve your warehouse operations.